The History of Computers
The History of Computers
 Description: An early mechanical computer demonstrating the initial steps in computational technology.
Description: An early mechanical computer demonstrating the initial steps in computational technology.
The history of computers is a fascinating journey that spans centuries, highlighting key innovations and milestones that have shaped modern computing.
Early Beginnings
The Abacus: One of the earliest tools used for computation, the abacus, dates back to around 2400 BC in Babylon. It was used for basic arithmetic calculations.
Charles Babbage and the Analytical Engine: Often considered the “father of the computer,” Charles Babbage conceptualized the Analytical Engine in the 1830s. Although never completed in his lifetime, this mechanical general-purpose computer laid the foundation for future innovations.
Ada Lovelace: Working with Babbage, Ada Lovelace is recognized as the first computer programmer. She wrote algorithms for the Analytical Engine and foresaw the potential of computers beyond mere calculation.
The Advent of Modern Computing
Alan Turing and the Turing Machine: In the 1930s, Alan Turing developed the concept of the Turing Machine, a theoretical device that could simulate the logic of any computer algorithm. This concept is fundamental to computer science.
ENIAC: The Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC), completed in 1945, was the first general-purpose electronic digital computer. It was used primarily for military calculations during World War II.
UNIVAC: The Universal Automatic Computer (UNIVAC), introduced in 1951, was the first commercially produced computer in the United States. It was used for business and government applications.
The Microprocessor Revolution
Intel 4004: Released in 1971, the Intel 4004 was the first commercially available microprocessor. It marked the beginning of the microcomputer revolution, making computers more accessible and affordable.
Personal Computers: The 1970s and 1980s saw the rise of personal computers (PCs), with iconic models like the Apple II, IBM PC, and Commodore 64. These machines brought computing power to homes and small businesses.
The Internet and World Wide Web: The development of the internet in the late 20th century, followed by the creation of the World Wide Web by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989, revolutionized how computers are used for communication, information sharing, and commerce.
The Modern Era
Smartphones and Mobile Computing: The early 21st century witnessed the rise of smartphones, combining computing power with mobile communication. Devices like the iPhone, introduced in 2007, transformed how people interact with technology.
Cloud Computing: Cloud computing, which allows users to access and store data and applications over the internet, has become a cornerstone of modern IT infrastructure. Companies like Amazon, Google, and Microsoft offer robust cloud services that support everything from personal file storage to enterprise-level applications.
Further Reading
For more detailed information on the history of computers, check out these resources:
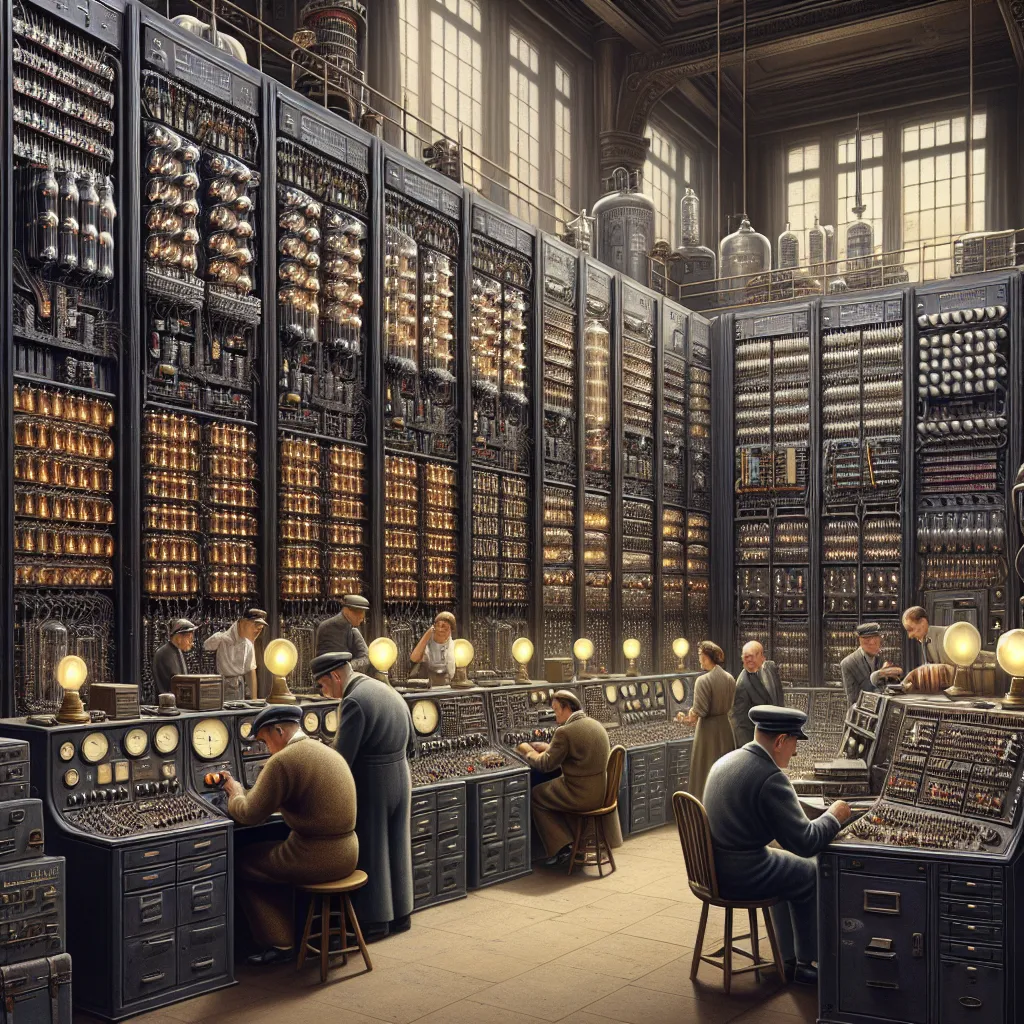 ENIAC, one of the earliest electronic general-purpose computers
ENIAC, one of the earliest electronic general-purpose computers
 Intel 4004, the first commercially available microprocessor
Intel 4004, the first commercially available microprocessor
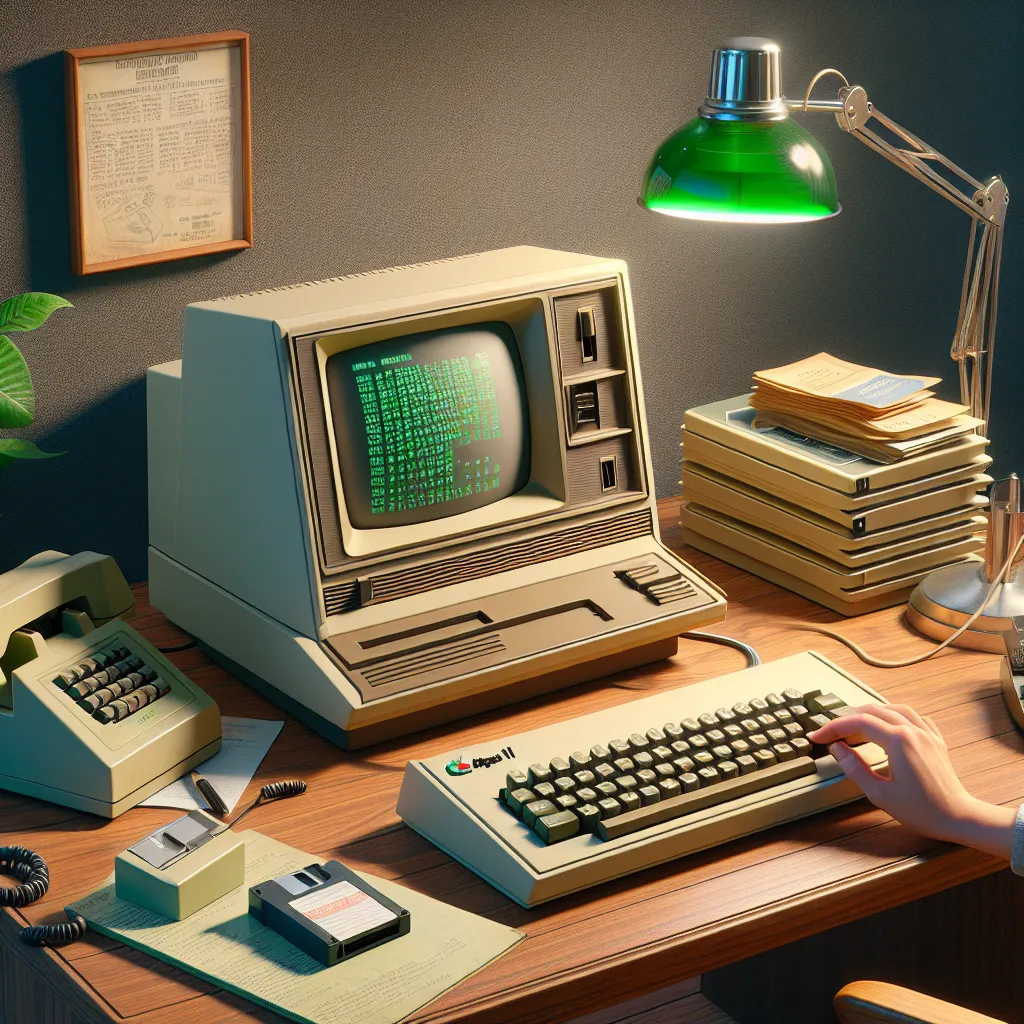 Apple II, a pivotal personal computer from the late 1970s
Apple II, a pivotal personal computer from the late 1970s
By exploring these resources, you can delve deeper into the milestones and figures that have shaped the development of computers from ancient times to the present day.